The Versatile ELT BlogA space for short articles about topics of interest to language teachers.
Subscribe to get notified of
|
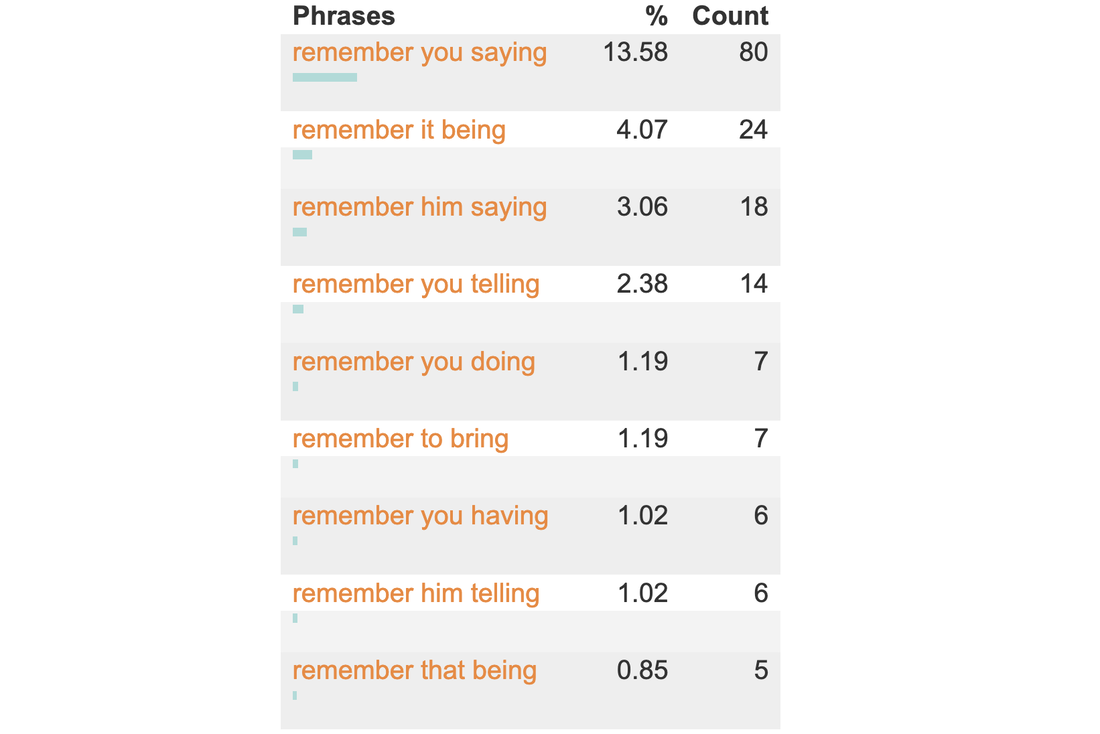
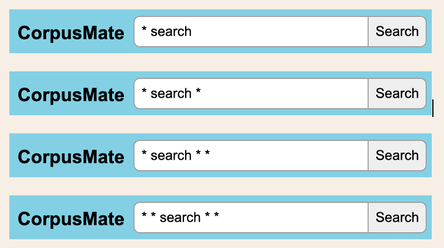
The mighty power of the asteriskFollowing on from my previous post about constellations, in this post I'm looking at the asterisk, which some of my students refer to as a star. I admit that that's a pretty tenuous connection and I apologise whole-heartedly. But the universe does get a mention here, so bear with me. I'm drafting a vocabulary workbook at the moment, or should I say yet another vocabulary workbook. In this one, the students are often tasked with discovering how words work in grammar patterns. They mainly use CorpusMate. This is quite a new, free, open-access and superfast corpus tool that was designed by Peter Croswaithe and programmed by Vit Baisa, who also programmed my VersaText and was instrumental in the development of SkELL. The CorpusMate corpus does not have part of speech tagging, which means that you can't search for a pattern such as Verb + noun + v-ing and there are hundreds of verbs in English that function in this pattern, e.g. remember, picture, catch, tolerate, leave. There are not only hundreds of words, but there are also hundreds of patterns that nouns, verbs and adjectives function in. My current vocabulary book revolves around the COBUILD grammar pattern reference books from the late 1990s. In fact, I wrote my masters dissertation on the grammar patterns of the verbs in the then new Academic Wordlist (2000) that Averil Coxhead had created for her masters dissertation. It is always interesting to see how much can be gleaned about the grammar pattern of a word without part of speech tags. The asterisk is mighty. In fact, it holds the secret to the meaning of life, the universe and everything. Read on! A supercomputer called Deep Thought was asked what the meaning of life, the universe and everything was. It calculated that it was 42. See the announcement in this extract from the film. Douglas Adams, the author of The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy, the cult 1979 novel from which this comes, always claimed that he chose the number 42 randomly. But 42 is the ASCII code for the asterisk, which in computer searches means anything and everything. Did Deep Thought calculate that the meaning of life, the universe and everything is anything and everything? This search uses two asterisks. The first has spaces before and after it, which makes the program search the corpus for all of the words in between the items to the left and the right of it. The second asterisk is used with a dot and is attached to ing. Dot-star, as my students call it. This makes the program search for words ending with ing. While this might include words such as thing and during, the fact is that the -ing word that follows remember followed by another word tends to be an -ing verb. This is the reality of pattern grammar. Click this link to see the first 250 of the 589 results of this search. This data is automatically sorted so that this pattern in the use of remember can be gleaned. To make these patterns even more visible and student friendly, clicking on the Pattern finder button generates a tidy table. Here are the top nine entries in that table. As mentioned, Verb + noun + -ing is one of hundreds of grammar patterns of words that the COBUILD team uncovered. They were not the first to identify this or many other patterns, but they were able to demonstrate with large corpora the semantic relationships between words that function in the same pattern. This means that the words in a grammar pattern are related in meaning. Important and interesting. Chunks Now back to our mighty asterisk! With queries such as these, you can find the frequent chunks that a target word is used in. The concordance extract below shows some things that people are "in search of a". I'm hoping that a vocabulary workbook that has students learning about the patterns that words function in and the words that go in these patterns through tasking them with discovering these properties of words for themselves using CorpusMate and other tools will be a stimulating voyage of discovery which will add a layer of systematicity to their vocabulary study which will in turn lead to them using words with more confidence and fewer hesitations. Think fluency. They might become stars themselves!
2 Comments
Alexcurd
8/1/2024 10:01:50
Thanks. This is all very nice. But it seems that most DDL activities are highly focused on showing the pattern but then, I usually get let down by them because there are no indications as to what things you do and how before and after the discovery of patterns (which will surely depend on their linguistic competence). For example, low-level learners will not be able to understand these patterns and will need much more pre-work on how these patterns form (via other resources, not direct DDL, which confuses them even more). Then, after DDL, they will need other types of activities to practice the linguistic input (e.g., based on corpus data, maybe by using chunks to be used in conversation, etc).
Reply
James Thomas
8/1/2024 13:10:00
Hi Alex. Yes, this is all very nice :-), thank you. I do understand your prevarications, but the thrust of this post basically concerns the use of the asterisk. I do not recommend using DDL with elementary learners. There are simply too many linguistic variables to juggle. I have actually tried myself in the foreign languages I learn.
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
To make a comment, click the title of the post.
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|